Sunday, August 31, 2014
Hard Disk Selector Wiring diagram Schematic

Switching from one operating system to another - that’s a risky business, isn’t it? Although this may be a bit of an exaggeration, the safest approach is still to install two different operating systems on the same PC, so you can always easily use the ‘old’ operating system if the new one fails to meet your needs (or suit your taste). A software solution is often used for such a ‘dual system’. A program called a ‘boot manager’ can be used to allow the user to choose, during the start-up process, which hard disk will be used for starting up the computer. Unfortunately, this does not always work flawlessly, and in most cases this boot manager is replaced by the standard boot loader of the operating system when a new operating system is installed.
In many cases, the only remedy is to reinstall the software. The solution presented here does not suffer from this problem. It is a hardware solution that causes the primary and secondary hard disk drives to ‘swap places’ when the computer is started up, if so desired. From the perspective of the computer (and the software running on the computer), it appears as though these two hard disks have actually changed places. This trick is made possible by a feature of the IDE specification called ‘CableSelect’. Every IDE hard disk can be configured to use either Master/Slave or CableSelect. In the latter case, a signal on the IDE cable tells the hard disk whether it is to act as the master or slave device. For this reason, in every IDE cable one lead is interrupted between the connectors for the two disk drives, or the relevant pin is omitted from the connector.

This causes a low level to be present on the CS pin of one of the drives and a high level to be present on the CS pin of the other one (at the far end of the cable). The schema shown here is connected to the IDE bus of the motherboard via connector K1. Most of the signals are fed directly from K1 to the other connectors (K2 and K3). An IDE hard disk is connected to K2, and a second one is connected to K3. When the computer is switched on or reset, a pulse will appear on the RESET line of the IDE interface. This pulse clocks flip-flop IC1a, and depending on the state of switch S1, the Q output will go either high or low. The state on the Q output is naturally always the opposite of that on the Q output. If we assume that the switch is closed during start-up, a low level will be present on D input of IC1a, so the Q output will be low following the reset pulse.

This low level on the Q output will cause transistor T1 to conduct. The current flowing through T1 will cause LED D1 to light up and transistor T2 to conduct. The hard disk attached to connector K2 will thus see a low level on its CS pin, which will cause it to act as the master drive and thus appear to the computer as the C: drive. A high level will appear on the Q output following the reset pulse. This will prevent T3 and T4 from conducting, with the consequence that LED D2 will be extinguished and the hard disk attached to connector K3 will see a high level on its CS pin. For this disk, this indicates that it is to act as a slave drive (D: drive).

If S1 is open when the reset pulse occurs, the above situation is of course reversed, and the hard disk attached to connector K2 will act as the D: drive, while the hard disk attached to connector K3 will act as the C: drive. Flip-flop IC1a is included here to prevent the hard disks from swapping roles during use. This could have disastrous consequences for the data on the hard disks, and it would most likely cause the computer to crash. This means that you do not have to worry about affecting the operation of the computer if you change the switch setting while the computer is running. The state of the flip-flop, and thus the configuration of the hard disks, can only be changed during a reset.
The schema is powered from a power connector for a 3.5-inch drive. This advantage of using this connector is that it easily fits onto a standard 4-way header. However, you must observe the correct polarity when attaching the connector. The red lead must be connected to pin 1. Constructing the hard disk selector is easy if the illustrated printed schema board is used. You will need three IDE cables to connect the schema. The best idea is to use short cables with only two connectors, with all pins connected 1:1 (no interruption in the CS line). The IDE connector on the motherboard is connected to K1 using one cable. A cable then runs from K2 to first hard disk, and another cable runs from K3 to the second hard disk. This means that it is not possible to connect more than two hard disks to this schema. You must also ensure that the jumpers of both disk drives are configured for CableSelect. To find out how to do this, refer to the user manual(s) for the drives.
4 x 6 5W QUAD POWER AMPLIFIER FOR CAR RADIO
MINIMUM EXTERNAL COMPONENT COUNT
HIGH CURRENT CAPABILITY
NO BOOTSTRAP CAPACITORS
NO BOUCHEROT CELLS
CLIP DETECTOR OUTPUT
HIGH OUTPUT POWER
HIGH APPLICATION FLEXIBILITY
FIXED GAIN
VERY LOW STAND-BY CURRENT (1µA typ)
NO SWITCH ON/OFF NOISE
Application circuit:
 |
| Circuit Diagram for TDA7370 |
 |
| pcb layout |
1992 Dodge w350 Wiring Diagram
 |
| 1992 Dodge w350 Wiring Diagram |
3 Input Video MUX Cable
Saturday, August 30, 2014
Simple DC Fan Controller
DC Fan Controller Circuit

Keep the Thermistor near the heat sink of the Amplifier PCB and switch on the amplifier for 10 minutes. Then adjust VR1 till the Fan stop running.When the temperature rises, Fan will automatically switch on.
Transmitter and Receiver Infra Red Headphone
| Transmiter schematics |
| Receiver schematics |
6N2P Tube Pre Tone Low Volt Low Cost Wiring diagram Schematic
The quality of their own personal thoughts of my own. Well honestly say that sometimes can get resistant. Instead of a 12AX7 plugged it by changing the pressure tube, topped only cycle . I try to create this Use only one tube. Working as a stereo (two halves of a single lamp), using low power as well.
6N2P Tube Pre-Tone Low Volt & Low Cost Circuit Diagram
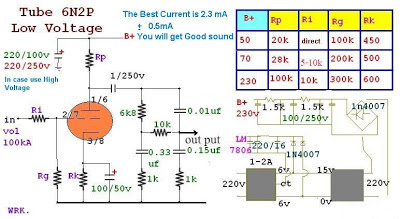
That if one wants to create a high fire. Put values as I get it offline because I reference values from the Data Sheet.
But do not suggest we fire up to 250 Volts Capacitor find the 350v. The price is expensive and over again.
I recommend creating a 230v. And then use the Cap 250 v. easy to find cheap used instead of the sound was no difference between voltage 250 to 230.

The trial was a pre-tone light bulb with + – 35 Volts with the famous schema 741. But output is not satisfactory offline … hum a lot. Experimental values are being changed. To complete the schema. Before, and I will be published offline because many people complained that the transformer is quite difficult to find ideas to this schema.
I do, then listen to the sound does not make sense at first, it offline. Central held very outstanding voice .. much agitation. But keep it open for a few days … to draw a lot more sense … mixing different sounds much less. Really listen. Voice is getting better offline …. now I’m comparing 12AX7. 6DJ8 6N2P 6N23P them on . wait a minute per well offline. Pictures show that I was to hear of the TDA2030 OTL 30watt.
Friday, August 29, 2014
Triac Light Switch as a dimers
If you want a light reception sensitivity of this circuit can be arranged then the 3.3 MOhm resistor can be replaced with a variable resistor. For more details can be seen from the following series of images.
 |
| Circuit Diagram |
Tone Control Tube Amp circuit with 12AU7
Schematic Power Amplifier with IC AN7112
See Schematic power amplifier (figure 1.1) and Package IC (figure 1.0) below :
 | ||
Figure 1.1 Click Image to View Enlarge
|
Low Voltage Remote Mains Switch

Thursday, August 28, 2014
Simple Gate Alarm
A cheap and simple gate alarm made from a single CMOS Integrated Circuit.

Cheap LED flasher Wiring diagram Schematic
TDA2002 Audio Ammplifier 10W
 |
| Circuit Diagram for TDA2002 Audio Ammplifier 10W |
Wednesday, August 27, 2014
Battery Powered High voltage Generator Wiring diagram Schematic
230 V AC To 400 V DC Power Supply Wiring diagram Schematic

A lot of students are who dont know how to convert 230 volt AC to 400 DC. So today i am published 230 V AC to 400 V DC schema diagram on my blog. Working principle of this schema diagram is very simple. You already knew the working principle of a bridge rectifier. This schema is same as bridge rectifier and the working principle is also same. The fuse is used to protect the schema, if the current is greater than 1 A.
Parts List
| Component No: | Value |
| F1 | 1 A |
| B1 | IN4007 |
| C1 | 470MF/450V |
| V1 | 230 V AC |
2 X 0 6W schematic audio amplifier
This schematic have require minimum voltage at 1Volt and maximum volotage at 9 Volt. Maximum output power 2 X 0.6W.

Part List:
Capacitor
C1 = 100uF
C2 = 220uF
C3 = 220uF
C4 = 220uF
C5 = 220uF
IC = ULN3782
Simple Readjust Shutdown Wiring diagram Schematic
Simple Readjust Shutdown Circuit Diagram

Simple Instrumentation Amplifier Wiring diagram Schematic

Tuesday, August 26, 2014
Build a Pulse Generator using Basic Operational Amplifier
The capacitor C1 1uF to change capacitance value by the frequency of 8 Hz, = 0.1uF 50Hz, 700Hz = 0.01uF, 0.001uF = 6kHz. In place of 1458 4558 may be used, LF353, etc.
| Add caption |
22 watt 12v audio Amplifier
This is a good news for the vehicle owners. Because This 22w audio amplifier works with 12v current.so you can use this one as an audio booster for your car set.And this schema gets only 60w .so you can operate your schema easily.when you operate this schema use 4 ohm speakers.8 ohm also works.The schema operates at 12 Volts at about 5 Amps at full volume.use a good heat sink for the chip.
Parts
U1 TDA1554 Two Channel Audio Amp Chip
R1 39K 1/4 Watt Resistor
C1,C2 10uf 25V Electrolytic Capacitor
C3 100uf 25V Electrolytic Capacitor
C4 47uf 25V Electrolytic Capacitor
C5 0.1uf 25V Ceramic Capacitor
C6 2200uf 25V Electrolytic Capacitor
Dancing LEDs

This is dancing LEDs schematic diagram. the LEDs will dance squence to audio (music or speaking) from the microphone.
Components list:
R1_____________10K 1/4W Resistor
R2,R3__________47K 1/4W Resistors
R4______________1K 1/4W Resistor
R5,R6,R7______100K 1/4W Resistors
R8____________820R 1/4W Resistor
C1,C3_________100nF 63V Ceramic or Polyester Capacitors
C2_____________10΅F 50V Electrolytic Capacitor
C4____________330nF 63V Polyester Capacitor (See Notes)
C5____________100΅F 25V Electrolytic Capacitor
D1___________1N4148 75V 150mA Diode
D2-D11_________5 or 3mm. LEDs (any type and color)
IC1___________LM358 Low Power Dual Op-amp
IC2____________4017 Decade counter with 10 decoded outputs IC
M1_____________Miniature electret microphone
SW1____________SPST miniature Slider Switch
B1_______________9V PP3 Battery
Clip for PP3 Battery
Additional schema parts (see Notes):
R9,R10_________10K 1/4W Resistors
R11____________56R 1/4W Resistor
D12,D13 etc.____5 or 3mm. LEDs (any type and color)
Q1,Q2_________BC327 45V 800mA PNP Transistors
Q3____________BC337 45V 800mA NPN Transistor
Circuit operation:
IC1A amplifies about 100 times the audio signal picked-up by the microphone and drives IC1B acting as peak-voltage detector. Its output peaks are synchronous with the peaks of the input signal and clock IC2, a ring decade counter capable of driving up to ten LEDs in sequence.
An additional schema allows the driving of up to ten strips, made up by five LEDs each (max.), at 9V supply. It is formed by a 10mA constant current source (Q1 & Q2) common to all LED strips and by a switching transistor (Q3), driving a strip obtained from 2 to 5 series-connected LEDs. Therefore one transistor and its Base resistor are required to drive each strip used.
Notes:
-
The sensitivity of the schema can be varied changing R4 value.
- C4 value can be varied from 220 to 470nF in order to change the schema speed-response to music peaks.
-
Adopting the additional schema, only one item for R10, R11, Q1 and Q2 is required to drive up to ten LED strips. On the contrary, one item of R9 and Q3 is necessary to drive each strip you decided to use.
-
Each R9 input must be connected to IC2 output pins, in place of the LEDs D2-D11 shown. R8 must also be omitted.
-
Whishing to use a lower number of LEDs or LED strips, pin #15 of IC2 must be disconnected from ground and connected to the first unused output pin. Example:
if you decided to use 5 LEDs, pin #15 of IC2 must be connected to pin #1; if you decided to use 8 LEDs, pin #15 of IC2 must be connected to pin #9 etc. -
Current drawing of the schema is about 10mA.
-
Whishing to use a wall-plug transformer-supply instead of a 9V battery, you can supply the schema at 12V, allowing the use of up to 6 LEDs per strip, or at 15V, allowing the use of up to 7 LEDs per strip.
Op Amp Audio Amplifier Wiring diagram Schematic
BH1417 Stereo FM Transmitter
Another important feature of this IC is that the transmission frequency seem like either set utilizing a 4 channel DIP switch. The IC seem like either powered in one anything between 4 to 6V DC and comes with other an output power around 20mW. At full output power the circuit consumes only 20mA and has a channel separation of 40dB. There {seem to be|appear to be|are} 14 possible preset transmission frequencies, starting in one 88.7MHz and incrementing in steps of 0.2MHz Which is going to be selected utilizing the DIP switch. The PLL circuitry of those IC is so precise that Theres almost no frequency drift.
Monday, August 25, 2014
Simple Flashing Lights Schematic
Circuit diagram :
Flashing Lights Schematic Circuit Diagram
Extend Timer Range For The 555
The schema shown here uses a 555 timer in the design but nevertheless achieves a timing interval of up to an hour! The trick here is to feed the timing capacitor not with a constant voltage but with a pulsed dc voltage. The pulses are derived from the un smoothed low voltage output of the power supply bridge rectifier.
Extend Timer Range For The 555 Circuit

The power supply output is not referenced to earth potential and the pulsing full wave rectified signal is fed to the base of T1 via resistor R1. A 100-Hz square wave signal is produced on the collector of T1 as the transistor switches.
The positive half of this waveform charges up the timing capacitor C1 via D2 and P1. Diode D2 prevents the charge on C1 from discharging through T1 when the square wave signal goes low. Push-button S1 is used to start the timing period. This method of charging uses relatively low component values for P1 (2.2 MΩ) and C1 (100 to 200 µF) but achieves timing periods of up to an hour which is much longer than a standard 555 schema configuration.
70W STK amplifier schematic
For this amplifier circuit using three voltage plus, min, and the ground. with a maximum voltage approximately 55Volt DC. And amplifier circuit can use some ic ie IC STK 030, 058, 075, 077, 078, 080, 082, 083, 084, 086. From all the ic I mentioned all of them can be applied to this amplifier circuit. But every ic whether there might be a different maximum voltage or power output, etc.. For this amplifier suitable for use at home, who need a voice soft and tasty. With a maximum output of 70W 8ohm impedance is my take of the highest IC output is STK086.Part List
R1 = 1K
R2 = 56K
R3 = 100R
R4 = 100R
R5 = 56K
R6 = 4.7R
R7 = 2.7K
C1 = 1uF
C2 = 470pF
C3 = 100uF
C4 = 100uF
C5 = 0.047uF
C6 = 47uF
C7 = 1800pF
C8 = 10uF
IC = STK 030, 058, 075, 077, 078, 080, 082, 083, 084, 086.
Police siren
The schema given here produces an alarm similar to the police siren. When you press the push button switch S2 capacitor C1 will charge and this will make the transistor Q1 to ON slowly. When the switch S1 is released the C1 will discharge and the transistor Q1 will become OFF slowly. When the Q1 is switched ON, its collector voltage falls and makes the transistor Q2 ON. The capacitor C2 will be charged almost to full supply voltage. This results in an increase in the collector-emitter voltage of Q2.This change in voltage is coupled to the base of Q1 via the capacitor C2.As a result the transistor Q1 comes slightly out of saturation. As a result the collector voltage of Q1 drops and makes the Q2 more OFF. This action continues until both transistors become OFF. Then the capacitor C2 discharges, and transistor Q1 will be switched ON again to start a new cycle. When the capacitor C1 is charged the tone will rise and when the capacitor C1 is discharging the tone will fall.
Notes.
* The schema can be assembled on a vero board.
* The schema can be powered from 9V DC.
* Switch S1 can be used as a power ON/OFF switch.
* K1 can be an 8 Ohm loud speaker.
High HiFi Power Amplifier with MOSFET
High Power Series HiFi Power Amplifier With MOSFET can modify to increase power output by doubling the final power amplifier is based on the diiginkan. Power generated from doubling the final power amplifier will also double its power output of power amplifier circuit "High Power HiFi Power Amplifier With MOSFET" it.
DC Power Supply Dual rail Variable Circuit
* Q1 and Q2 must be mounted on heatsinks. Usually, bolting them to the metal case (through insulating washers etc.) proved effective.
* The full ±15V output can be achieved only if the secondary winding of the supply Transformer used in the Variable DC Power Supply is rated at 48V minimum (center tapped).
* When using this schema, please set the Current-limit control (P1) of the Variable DC Power Supply to any value comprised in the 50mA - 1A range but not higher.
* The second Op-amp (IC1B) contained in the LM358 chip was not used, but its input pins were tied to the negative supply and the output was left open.
DC Power Supply Dual-rail Variable Part list:
R1 = 4.7K-1/2W
R1 = 4.7K-1/2W
C1 = 100nF-63V
C2 = 220µF-25V
C3 = 220µF-25V
C4 = 100nF-63V
C5 = 100nF-63V
Q1 = BD437
Q2 = BD438
IC1 = LM358
Sunday, August 24, 2014
One IC Transmitter Wiring diagram Schematic

Free Circuit Diagrams 4U has given you many transmitter schema diagrams today Im going to give you some transmitter schema with some modifications.This schema can send signals up to 100 M.Here we have used IC UPC 1651.This schema can be operated with 6V.The special thing of this schema is we can build this schema with one IC.

Note :
# Build this schema with 6V power supply
# Build this schema on a PCB
IC 555 Tester Circuits
Complete circuit tester 555 as follows.

source:link
4 20 Volts Amplifier Circuit
Schematic Audio Amplifier with IC TDA2030

Efficient Fan Speed Controller Wiring diagram Schematic
Kicad Software

1. main applications:
• Project manager kicad, allowing you to create and configure new works;
• electrical circuits eeschema editor for drawing and komponirovaniya schemes, including the editor of characters;
• PCB editor pcbnew, forming electric circuits and circuit comprising editor seats
2. additional utilities:
• file viewer format Gerber - gerbview;
• a program to identify seats according to the components on the circuit - cvpcb;
• Editor view reports wyoeditor.
Furthermore KiCad includes a plurality of libraries of electronic components for which there is formed a three-dimensional model Wings3D program.

Disadvantages of the system design is attributed uncomfortable and intuitive interface. Program difficult to master without reading the documentation.

Saturday, August 23, 2014
Simple SGI Amplifier Wiring diagram Schematic
Simple SGI Amplifier Circuit Diagram
8 Watt Audio Amplifier

Component List:
C1 - 10uf Electrolytic Capacitor
C2 - 470uf Electrolytic Capacitor
C3 - 0.1uF Disc Capacitor
C4 - 2000uf Electrolytic Capacitor 2200uF
R1 - 2.2 Ohm Resistance (Anything Within 10% tolerance)
R3 - 220 Ohm Resistance (Anything Within 10% tolerance)
IC1 - LM383 IC
