Learning Programming MCS51 becomes mandatory we learn if we want to use the MCS51. In the first part of this Learning Programming MCS51 we will learn together about the basic programming language MCS51 microcontroller. Where to program MCS51 outline there are 2 core parts of pemrogramanya language is "Words Work" and "Object". In the article Programming MCS51 this first part we will study first the "verb" is a command group Peng-copies of data, the command group arithmetic and logic command group.
Reference to DATA IN PROGRAMMING MCS51
Data can be in many different places, thus known a few ways to describe the data (in English often referred to as Addressing Mode), among others, as follows:
The mention of constant data (immediate addressing mode): MOV A, # $ 20. Constant data is data that was in the instructions. Examples of this instruction has the data meaning a constant $ 20 (as a constant data marked with #) on-copy it into the accumulator A. What needs to be properly addressed in this order is the number $ 20 is part of the instruction.
Reference to data directly (direct addressing mode), this method is used to refer to data residing in memory by calling the memory number where the data are: MOV A, $ 30. Examples of these instructions have the meaning of data in the memory number $ 30 in-copy it to the accumulators.
At first glance these same instructions to the instruction constant data above, the difference above instructions using the # which marks the $ 20 is a data constant, whereas in this instruction because there was no sign # then $ 30 is a number from memory.
The mention of indirect data (indirect addressing mode), this method is used to refer to data residing in memory, if memory data storage is changing its location so that the memory number is not called directly but in-titip her into another register : MOV A, @ R0.
In this instruction versatile R0 register is used to record the number of memory, so that this instruction has a memory meaning that the number recorded in the contents of R0-copy it into the accumulator A.
Sign @ is used to mark the memory number stored in R0.
Compare this with the instruction memory number directly mention above, in this instruction first memory numbers are stored in R0 and R0 appoint a role which memory is used, so that if the value of R0 change the designated memory will also be changed as well.
In this instruction registers R0 functioning multipurpose container for the address register (indirect address register), other than all-purpose registers R0 R1 can also be used as a container for the address register.
Reference to data in the register (register addressing mode): MOV A, R5. This instruction has the meaning of data in all-purpose register R5 is copy it into the accumulator A. This instruction makes all-purpose registers R0 to R7 as a place to store data that is very practical that it works very fast.
The data referred to in the discussion above all in the data memory (including all-purpose registers are also located in data memory). In writing the program, often required standard table that is stored along with the program. Tables of this kind is really a data residing in program memory!
For this purpose, MCS51 have any mention of data in memory means programs conducted by indirect (indirect addressing code mode): MOVC A, @ A + DPTR.
Notice in this MOV instruction is replaced with MOVC, the additional letter C is meant to distinguish that this instruction is used in the program memory. (MOV without the letter C means that the instruction used in the data memory).
Sign @ is used to mark A + DPTR is used to indicate the number of contents in-memory copy it to the accumulator A, in this case the value stored in the DPTR (Data Pointer Register - 2 bytes) plus the value stored in accumulators A (1 byte) is used to refer to the program memory numbers.
Verb in AT89Cx051
Overall AT89Cx051 have as many as 255 kinds of instruction, which was formed by combining the verb and objects. "The verb is the group discussed the following:
PENG GROUP-COPY-DATA AN MCS51
Basic code for this group are MOV, abbreviation of MOVE, which means to move, though more correct to say this command have meaning copying the data. This can be explained the following: after the instruction MOV A, R7 done, accumulators A and all-purpose register R7 contains the same data, originally stored in R7.
MOV command is distinguished according to the type of memory AT89Cx051. This command is on the memory data is written into MOV, for example:
MOV A, $ 20
MOV A, @ R1
MOV A, P1
MOV P3, A
To use the program memory, this command is written into MOVC, there are only 2 types of wear MOVC instructions, namely:
MOVC A, @ A + DPTR; DPTR as register indirect
MOVC A, @ A + PC, PC as the register indirect
In addition, there is also known MOVX command, the command that is used for external data memory (X singkatakan from External). This command is only available to the MCS51 family members who have an external data memory, for example AT89C51 and so forth, and certainly not known by the group that tidam AT89Cx051 have external data memory. There are only 6 kinds of wear MOVX instruction, these instructions are:
MOVX A, @ DPTR
MOVX A, @ R0
MOVX A, @ R1
MOVX @ DPTR, A
MOVX @ R0, A
MOVX @ R1, A
GROUP ARIMATIK (ADD, ADDC, SubB, DA, MUL and DIV)
ADD and ADDC command
The contents of accumulators A plus the number 1 byte, the sum will be collected back in the accumulator. In this operation Carry bit (C flag in the PSW - Program Status Word) serves as a reservoir overflow of the sum. If the sum of the abundance (a value greater than 255) will carry bit value 1 , if not Carry bit value 0. ADDC same with ADD, only in bits Carry ADDC value in the previous process involved summed together.
Numbers 1 byte is added to the accumulator, can be derived from a constant, from the all-purpose register, memory data from memory number is called directly or indirectly, as shown in the following example:
ADD A, R0; register versatile
ADD A, # $ 23; a constant
ADD A, @ R0; no memory indirect
ADD A, P1; no direct memory (port 1)
ORDERS IN PROGRAMMING SubB MCS51
The contents of Accumulator A less the number 1 byte follows with Carry bit value, the reduction will be accommodated again in the accumulators. Carry bits in this operation also serves as a reservoir overflow of the reduction. If the reduction is abundant (score less than 0) bits Carry would be worth 1 , if not Carry bit value 0.
SubB A, R0; A = A - R0 - C
SubB A, # $ 23; A = A - $ 23
SubB A, @ R1
SubB A, P0
DA command
DA command (Decimal Adjust) is used after the command ADD, ADDC, or SubB, used to convert 8-bit binary value stored in the accumulator into 2 pieces decimal number, each consisting of 4-bit binary value.
MUL AB ORDERS IN PROGRAMMING MCS51
8-bit binary number in accumulator A is multiplied by an 8-bit binary number in register B. The result of multiplication of binary 16-bit, 8 bit binary number that greater weight be accommodated in the register B, while the other 8 bits are accommodated in the smaller weight accumulator A.
OV bit in the PSW (Program Status Word) is used to mark the result of multiplying the existing value in register B. OV bit will be worth 0 if register B is worth $ 00, if not worth OV bit 1.
MOV A, # 10
MOV B, # 20
MUL AB
DIV AB ORDERS IN PROGRAMMING MCS51
8-bit binary number in accumulator A is divided by an 8-bit binary number in register B. The result of the division of 8-bit binary numbers stored in the accumulator, while the rest of the division of 8-bit binary number stored in register B.
OV bit in the PSW (Program Status Word) is used to mark the value before the division that exists in the register B. OV bit will be worth 1 if register B originally worth $ 00.
GROUP LOGIC (ANL, ORL and XRL) IN PROGRAMMING MCS51
This command group used to perform logic operations MCS51 microcontroller, logic operations can be done is the AND operation (operation code ANL), OR operation (operation code ORL) and the Exclusive-OR operation (XRL operation code).
The data used in this operation can be data that is in the accumulator or data that are in-memory data, this is a little different with arithmetic operations that must be actively melihatkan accumulators.
Operating results are accommodated in the first data source.
AND logic operation is widely used to me 0 a few specific bits of an 8-bit binary number, the way to forming an 8-bit binary numbers as a data-ANL constant in a number of origin. Bit-0 want in a represented by 0 in constant data, while other bits given the value 1, eg
Instructions ANL P1, #% 01111110 will result in bit 0 and bit 7 of Port 1 (P1) value 0 while the other bits remain unchanged in value.
OR logic operation is widely used to me 1 a few specific bits of an 8-bit binary number, the way to forming an 8-bit binary numbers as constant data in a number-ORL origin. Bit-1 want in a represented by 1 in constant data, while other bits given the value 0, eg
Instructions ORL A, #% 01111110 will result in bit 1 to bit 6 of the accumulator value 1 while other bits remain unchanged in value.
Exclusive-OR logic operation is widely used to reverse the value (complement) some particular bits of an 8-bit binary number, the way to forming an 8-bit binary numbers as constant data in a number-XRL origin. Bit you want behind-the value represented by 1 in constant data, while other bits are the value 0, eg
Instructions XRL A, #% 01111110 will result in bit 1 to bit 6 of the accumulator turned value, while other bits remain unchanged in value.
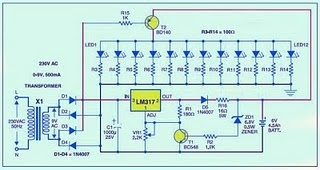
 The ESR Meter is basically an AC Ohmmeter with special scales and protective circuitry. It provides a continuous reading of series resistance in electrolytic capacitors. It operates at 100 kHz to keep the capacitive reactance factor near zero. The remaining series resistance is due to the electrolyte between the capacitor plates and indicates the state of dryness. Capacitor termination problems also show up plainly due to the continuous ohmic reading.
The ESR Meter is basically an AC Ohmmeter with special scales and protective circuitry. It provides a continuous reading of series resistance in electrolytic capacitors. It operates at 100 kHz to keep the capacitive reactance factor near zero. The remaining series resistance is due to the electrolyte between the capacitor plates and indicates the state of dryness. Capacitor termination problems also show up plainly due to the continuous ohmic reading. The ESR meter uses 8 operational ainplifiers. An op-amp is an idealized basic amplifier with two inputs. The non-inverting input (+) has an in-phase relationship with the op-amp output, and the inverting input (-) an out-of-phase relationship. Op-amps are usually used with negative feedback and reach a stable operating condition when their two inputs are equal in voltage.
The ESR meter uses 8 operational ainplifiers. An op-amp is an idealized basic amplifier with two inputs. The non-inverting input (+) has an in-phase relationship with the op-amp output, and the inverting input (-) an out-of-phase relationship. Op-amps are usually used with negative feedback and reach a stable operating condition when their two inputs are equal in voltage. Op-amps IA & 1B form a regenerative 100 kHz oscillatnr circuit. Capacitor C1 is the basic tiining capacitor and RI is selected to set frequency. Diodes D2 & D3 clip the bottom and top of the output waveform so that the output level and frequency are resistant to battery voltage changes.
Op-amps IA & 1B form a regenerative 100 kHz oscillatnr circuit. Capacitor C1 is the basic tiining capacitor and RI is selected to set frequency. Diodes D2 & D3 clip the bottom and top of the output waveform so that the output level and frequency are resistant to battery voltage changes.






.JPG)







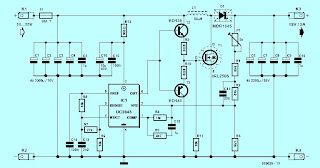
 This circuit reproduces the starting light sequence currently used by FISA for Formula One racing. It could be used with slot car sets (such as HO scale AFX/Life Like/Tyco sets) or radio controlled cars. IC1, a 555 timer IC, is used as a clock pulse generator. Its output is fed via NAND gates IC2a and IC2c to IC3, a 4024 binary counter. IC2b inverts the O4 output of 4024 binary counter IC3. Initially, IC3 is reset and all its outputs are low, including O4, which causes IC2b to present a logical high to the pin 8 input of IC2c which then passes pulses from the 555 clock circuit to the clock input of the 4024. IC3 then begins counting.
This circuit reproduces the starting light sequence currently used by FISA for Formula One racing. It could be used with slot car sets (such as HO scale AFX/Life Like/Tyco sets) or radio controlled cars. IC1, a 555 timer IC, is used as a clock pulse generator. Its output is fed via NAND gates IC2a and IC2c to IC3, a 4024 binary counter. IC2b inverts the O4 output of 4024 binary counter IC3. Initially, IC3 is reset and all its outputs are low, including O4, which causes IC2b to present a logical high to the pin 8 input of IC2c which then passes pulses from the 555 clock circuit to the clock input of the 4024. IC3 then begins counting. 
